Top 10 Uses of Chromium in Electroplating You Need to Know
In the world of industrial processes, one element stands out for its exceptional properties: chromium. Widely recognized for its durability and resistance to corrosion, chromium is used for electroplating in various applications, from automotive to aerospace. Industry expert Dr. Michael Smith, a renowned metallurgist, highlights the significance of this process by stating, "The use of chromium in electroplating not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of components but also extends their functional lifespan."
As we delve into the top ten uses of chromium in electroplating, it becomes evident that this versatile metal plays a crucial role in improving surface properties, ensuring products can withstand harsh environments while maintaining their integrity. From offering a brilliant shine to providing a protective layer against wear and tear, the applications of chromium-plated surfaces are extensive and vital in today’s technological landscape.
Understanding the myriad ways in which chromium is used for electroplating helps industries innovate and optimize their manufacturing processes. As we explore these uses, we will uncover how this remarkable metal contributes not just to the performance of products, but also to advancements in various sectors, showcasing its undeniable value in modern applications.

What is Electroplating and Its Importance in Modern Manufacturing
Electroplating is a pivotal process in modern manufacturing, involving the application of a metallic coating to a surface through electrochemical procedures. This technique not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of products but also significantly improves their durability and resistance to corrosion. By depositing a layer of metal, such as chromium, onto a base material, manufacturers can achieve desired surface properties, including increased hardness and reduced friction. The importance of electroplating lies in its ability to extend the lifespan of components, thereby decreasing the need for frequent replacements and contributing to more sustainable manufacturing practices.
In addition to improving physical properties, electroplating plays a crucial role in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and electronics. In the automotive sector, for example, chrome-plated parts are not only visually striking but also serve to protect critical components from wear and environmental damage. Furthermore, electroplating can be tailored to meet specific functional requirements, allowing engineers to design products that are both innovative and reliable. As technology advances, the significance of electroplating continues to grow, positioning it as an essential technique for achieving high-performance manufacturing solutions.
Top 10 Uses of Chromium in Electroplating
Overview of Chromium as a Material in Electroplating Processes
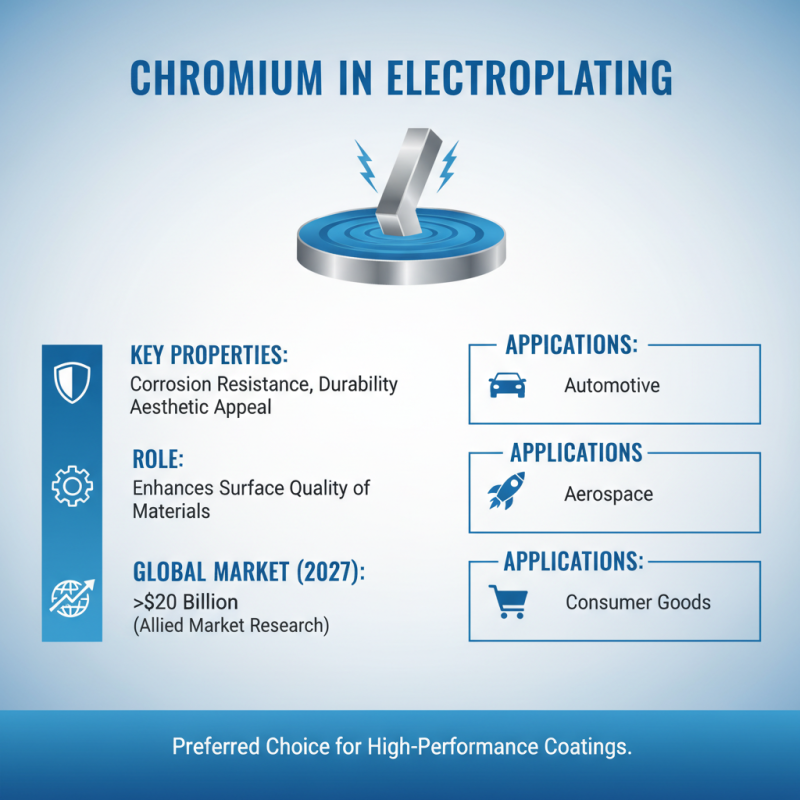
Chromium plays a pivotal role in electroplating processes due to its unique properties, including high corrosion resistance, durability, and aesthetic appeal. As a transition metal, chromium is valued for its ability to enhance the surface qualities of materials, making it a preferred choice for coatings across various industries. According to a recent market analysis report from Allied Market Research, the global electroplating market is projected to reach over $20 billion by 2027, with chromium-based processes contributing significantly due to their performance characteristics in automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods applications.
In electroplating, chromium can be deposited as either hard chrome or decorative chrome. Hard chrome plating is essential for protecting components from wear and tear, particularly in industries like manufacturing and aerospace. It offers a sturdy barrier against oxidation and mechanical stress, which is crucial for the longevity of parts. Conversely, decorative chrome provides a high-gloss finish that not only enhances visual appeal but also adds a layer of protection against corrosion. As per the latest industry research, chromium's contribution to electroplating applications is expected to grow, driven by increasing demands for durable and aesthetically pleasing finishes.
Tips: When selecting a chromium electroplating service, it is essential to consider the specific requirements for your application. Understanding the differences between hard and decorative chrome can help you make informed decisions tailored to your needs. Additionally, regularly maintaining plated surfaces can significantly prolong their lifespan and performance, ensuring that you maximize your investment in chromium coatings.
Top 10 Applications of Chromium in Various Industries
Chromium, a versatile transition metal, plays a crucial role across various industries, particularly in electroplating applications. One of its most significant uses is in the automotive sector, where chromium plating provides both aesthetic value and increased corrosion resistance to exposed metal parts. According to a report by Markets and Markets, the global automotive electroplating market is expected to reach USD 10.5 billion by 2026, with chromium plating being a key contributor due to its durability and ability to enhance metal's appearance.
In addition to automotive applications, chromium is widely utilized in the aerospace industry for components that require exceptional strength and resistance to wear and corrosion. A study published by Research and Markets highlights that the aerospace electroplating market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.2% from 2021 to 2026, with chromium playing an integral role in the production of lightweight yet strong materials essential for aircraft safety and efficiency.
Furthermore, in the electronics industry, chromium coatings are increasingly used in connectors and other components to improve electrical conductivity while providing protection against oxidation, enhancing the longevity and performance of electronic devices.
Benefits of Using Chromium in Electroplating Techniques
Chromium plays a crucial role in electroplating techniques, primarily due to its exceptional properties that enhance the durability and aesthetic appeal of metal surfaces. One of the key benefits of using chromium in electroplating is its ability to provide a hard, protective layer that resists corrosion and wear. This is particularly important in industries where components are exposed to harsh environments, as a chromium layer can significantly extend the lifespan of products, thereby reducing maintenance costs and increasing reliability.
In addition to its protective capabilities, chromium also contributes to the visual appeal of electroplated items. Its brilliant, mirror-like finish not only enhances the overall appearance of products but also adds value by making them more attractive to consumers. Furthermore, the use of chromium in electroplating allows for excellent adhesion of the plating material, ensuring a robust bond between the substrate and the plated layer. This combination of aesthetic enhancement and functional protection makes chromium an indispensable element in various electroplating applications, from automotive parts to household appliances.
Top 10 Uses of Chromium in Electroplating You Need to Know
| Use | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive Parts | Chromium is used to electroplate automotive parts for corrosion resistance and aesthetics. | Improved durability and a shiny finish. |
| Household Items | Common in items like faucets and fixtures to enhance appearance and longevity. | Luxurious look and enhanced lifespan. |
| Industrial Equipment | Used for components subjected to harsh environments. | Increased resistance to wear and tear. |
| Electrical Contacts | Chromium plating improves conductivity in connectors and contacts. | Enhanced performance and reduced corrosion. |
| Kitchen Utensils | Electroplated cutlery and cookware for a sleek finish. | Aesthetic appeal and resistance to rust. |
| Jewelry | Chromium is used to coat jewelry for additional shine. | Brighter appearance and better scratch resistance. |
| Medical Instruments | Utilized in surgical instruments to prevent corrosion. | Increased hygiene and longevity. |
| Construction Materials | Chromium plating is used on tools and fasteners in construction. | Enhanced strength and wear resistance. |
| Hardware Components | Common in locks, handles, and hinges. | Increased durability and a modern look. |
| Optical Instruments | Used in the coating of optical devices for improved clarity. | Better transparency and reduced glare. |
Environmental Considerations and Safety Measures for Chromium Use

Chromium is widely utilized in electroplating due to its exceptional corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. However, the environmental implications of chromium use are significant, necessitating careful consideration. Studies indicate that hexavalent chromium, the form commonly used in electroplating, poses serious health risks, including respiratory issues and skin irritations, which can arise from exposure. According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), chromium emissions from electroplating operations contribute to air and water pollution, prompting stringent regulatory measures. Thus, industries must implement effective containment and filtration systems to minimize environmental impact.
In addition to air quality concerns, wastewater management is critical in electroplating processes involving chromium. The presence of heavy metals in effluents can severely affect aquatic ecosystems, leading to biodiversity loss. The World Health Organization (WHO) has highlighted that improper disposal of chromium-laden waste can result in contaminated drinking water, posing risks to human health. The adoption of closed-loop systems and advanced treatments, such as ion exchange and reverse osmosis, is essential for reducing chromium discharge into the environment. Overall, ensuring proper safety measures and environmental management practices is crucial for industries to mitigate risks associated with chromium electroplating while maintaining compliance with health and safety regulations.
Related Posts
-

2025 Top Guide to Cobalt Plating Techniques and Applications
-
2025 Top Industrial Chrome Plating Techniques Benefits and Applications
-

10 Essential Tips for Successful Industrial Chrome Plating You Need to Know
-

Top 10 Tips for Successful DIY Chrome Plating at Home
-
2025's Top Chrome Plating Techniques: Enhance Durability and Aesthetics
-

Top 10 Benefits of Industrial Hard Chrome Plating for Enhanced Durability
