Why Consider Alternatives to Hard Chrome Plating for Your Industry Needs
In the pursuit of maximizing efficiency and sustainability in manufacturing, many industries are exploring alternatives to hard chrome plating. This shift is not just a trend but a necessary adaptation as environmental regulations tighten and the search for safer, more effective coating solutions intensifies. Renowned expert Dr. Emily Thompson, a leading voice in surface engineering, emphasizes the importance of this transition by stating, "Choosing an alternative to hard chrome plating can significantly enhance both the performance and ecological footprint of industrial components."
Alternative coatings such as nickel-boron, ceramifiable coatings, and thermal spraying not only meet the stringent demands for wear and corrosion resistance but also offer additional benefits like reduced toxicity and improved adhesion. As industries continuously seek methods that align with sustainability goals while maintaining product quality, reevaluating traditional methods like hard chrome plating is crucial. Embracing these innovative solutions can lead to both operational benefits and compliance with evolving environmental standards, making the exploration of alternatives to hard chrome plating a pivotal conversation for today's industries.
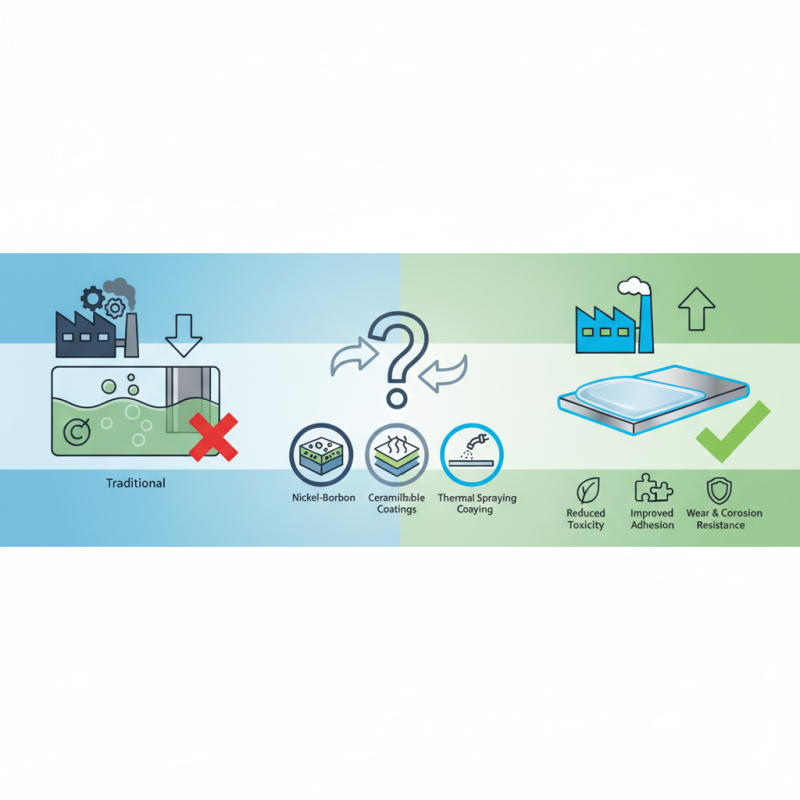
Benefits of Alternative Coatings Over Hard Chrome Plating in Manufacturing
In manufacturing, hard chrome plating has been a longstanding choice for enhancing surface properties like corrosion resistance and wear performance. However, there are several alternative coatings that provide significant advantages over traditional hard chrome. For instance, coatings such as thermal spray alloys and ceramic-based finishes not only deliver superior hardness but also offer enhanced thermal stability and better performance in extreme environments. These alternatives can exceed the lifespan of hard chrome while requiring less frequent maintenance, leading to increased operational efficiency.
Moreover, many alternative coatings are designed to be environmentally friendly, reducing the hazardous waste associated with the hard chrome plating process. Techniques such as pulsed plasma spray or electrodeposition of sustainable materials allow for a more eco-conscious approach without sacrificing performance. Additionally, the versatility of these emerging coatings in terms of customization, thickness, and application methods make them more suitable for a diverse range of industrial applications. As industries strive for both efficiency and sustainability, considering alternatives to hard chrome plating is not just beneficial but essential for long-term success.
Environmental Regulations Impacting Hard Chrome Plating Across Industries
The implications of environmental regulations on hard chrome plating are becoming increasingly significant across various industries. The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and similar regulatory bodies worldwide have implemented stringent guidelines to limit the release of hexavalent chromium, a toxic compound often found in hard chrome plating processes. According to a report by the National Association for Surface Finishing, compliance with these regulations has led to an increase in operational costs for many businesses that rely on hard chrome plating due to necessary investments in advanced filtration and waste treatment technologies.
Moreover, the rise of more sustainable alternatives is reshaping market dynamics. For instance, electroplating and thermal spray coatings are steadily gaining traction as viable substitutes. A study by the Surface Engineering Association indicates that these alternatives not only meet regulatory standards but also offer comparable, if not superior, performance in terms of wear resistance and surface finish. Industries such as aerospace and automotive are particularly affected, where the push for more environmentally friendly solutions aligns with their commitment to reducing overall carbon footprints. A shift towards these alternatives could potentially reduce compliance costs and encourage innovation in surface treatment processes, reflecting a broader trend towards sustainability across manufacturing sectors.
Why Consider Alternatives to Hard Chrome Plating for Your Industry Needs
| Industry | Alternative Coating Option | Environmental Impact | Regulatory Compliance | Cost Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Electroless Nickel | Lower toxicity compared to chrome | Meets FAA regulations | Moderate initial investment |
| Automotive | Thermal Spray Coatings | Reduced hazardous waste | Compliant with EPA standards | Higher maintenance costs |
| Manufacturing | Zinc-Nickel Alloy | Less environmental hazard | Meets ISO 14001 standards | Cost-effective over time |
| Oil and Gas | Ceramic Coatings | Minimized toxic emissions | Strictly regulated | Higher upfront cost |
| Electronics | PVD Coatings | Low environmental footprint | ENVIRO compliant | Higher machine costs |
Performance Comparison: Hard Chrome Plating vs. Alternative Surface Treatments
When evaluating surface treatments for industrial applications, it's essential to conduct a performance comparison between hard chrome plating and alternative methods. Hard chrome plating has long been favored for its excellent wear resistance, corrosion protection, and low friction properties. However, it is not without limitations, such as its environmental impact and the potential for cracking and peeling under stress. These drawbacks have led many industries to explore other options that may offer similar or superior performance without the associated downsides.
Alternative surface treatments, such as electroless nickel plating, anodizing, and ceramic coatings, present a range of benefits that can better meet specific requirements of various applications. For instance, electroless nickel plating delivers uniform coverage even on complex geometries, enhancing corrosion resistance and reducing friction. Anodizing, primarily used on aluminum, improves surface hardness and can be tailored to provide additional colors or finishes, while ceramic coatings are increasingly popular for their thermal resistance and durability in extreme conditions. Each of these alternatives offers unique properties that can outperform hard chrome plating, making them a compelling choice for businesses seeking innovative solutions for their industrial needs.
Performance Comparison: Hard Chrome Plating vs. Alternative Surface Treatments
Cost Analysis of Hard Chrome Plating Versus Modern Alternatives
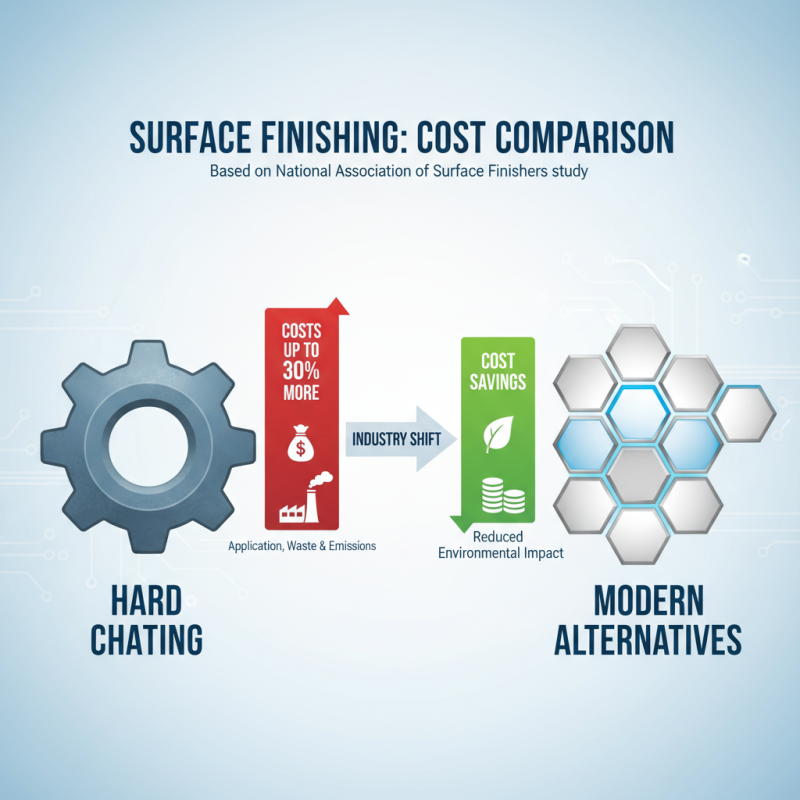
In recent years, industries have been increasingly scrutinizing the cost implications of hard chrome plating compared to modern alternatives. While hard chrome plating has been a longstanding method for enhancing wear resistance and surface hardness, it carries significant costs associated with both application and environmental compliance. According to a study by the National Association of Surface Finishers, the overall expenditure on hard chrome plating can be as high as 30% more than on newer surface treatment technologies when considering not only the direct costs but also the expenses related to waste disposal and emissions control.
On the other hand, advanced surface finishing technologies, such as thermal spray coatings and electroless nickel plating, not only offer competitive performance but also demonstrate reduced operational costs. A report from the European Coatings Journal indicates that these modern alternatives can decrease overall lifecycle costs by approximately 20-40%. Additionally, they often come with enhanced durability and resistance to corrosion, thus extending the service life of components, which is a critical consideration for industries focused on efficiency and sustainability. By weighing these cost factors, decision-makers can better align their operational strategies with both financial performance and environmental responsibility.
Latest Innovations and Technologies in Surface Coatings for Industrial Use
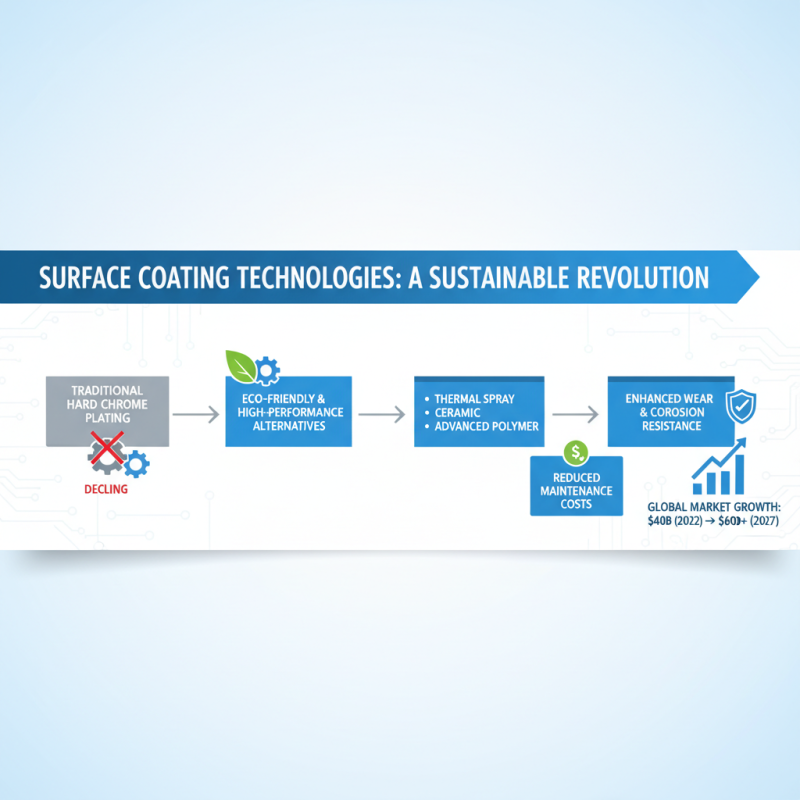
The advancement of surface coating technologies is revolutionizing industries, shifting focus from traditional hard chrome plating to more innovative and sustainable solutions. Recent studies indicate that the global surface coatings market is projected to grow from $40 billion in 2022 to over $60 billion by 2027, driven by the increasing demand for eco-friendly and high-performance alternatives. These alternatives, such as thermal spray coatings, ceramic coatings, and advanced polymer coatings, not only enhance wear resistance but also provide significant improvements in corrosion resistance, reducing maintenance costs for various industries.
One of the key trends in surface coatings is the integration of nanotechnology, which has shown a remarkable potential to enhance properties at the molecular level. According to a report by Engineering Industries, nanoparticles can increase the hardness and lifespan of coatings by up to 50%. Additionally, coatings designed with self-healing properties are gaining popularity, offering the ability to repair surface damage autonomously and extending the useful life of industrial components significantly.
Tips: When considering alternatives to hard chrome plating, assess the specific performance requirements of your application. Look for surface coatings that provide a balanced approach to toughness and flexibility, ensuring adaptability to various environmental conditions. Consider engaging with technology providers who can offer a comprehensive analysis of how different surfaces can meet your operational needs while adhering to sustainability practices.
Related Posts
-

Top 10 Benefits of Industrial Hard Chrome Plating for Enhanced Durability
-

What is Decorative Plating and How Does it Enhance Product Aesthetics
-
2025 Top Industrial Chrome Plating Techniques Benefits and Applications
-

2025 Top Guide to Cobalt Plating Techniques and Applications
-
2025's Top Chrome Plating Techniques: Enhance Durability and Aesthetics
-

Ultimate Guide to Bright Chrome Plating Benefits Techniques and Applications
